Psoriasis is a long-term and practically incurable disease that is not contagious. It mainly affects the skin, nails, and joints. Psoriasis can occur in a person of any age, even in children.
There are several theories about the cause of psoriasis:
- Theory of neurogenic disorders;
- Theory of problems in the endocrine system;
- Theory of viral disorders or the theory of metabolic disorders.
But none of these theories have been scientifically proven. To date, scientists have come to the conclusion that the onset of the disease is due to the influence of genetics or a person's genetic predisposition to pathological changes in skin cells.
These cells are formed in the basal layer and reach the outer stratum corneum, forming scales. Genetic factors indicate the presence of the disease in relatives. In other words: if your loved one has psoriasis, it could show up in you or your children.
Factors that affect the appearance of psoriasis
The following factors influence the occurrence of psoriasis:
- Neurasthenia;
- Mental and physical shock, overload of the body;
- Diseases of the endocrine system;
- Biochemical and enzymatic disorders;
- Hypothermia of the body;
- Reduced immunity.
It is difficult to determine and confirm what caused the disease. They often say that the disease appears for no apparent reason.
What is psoriasis: how does it manifest?
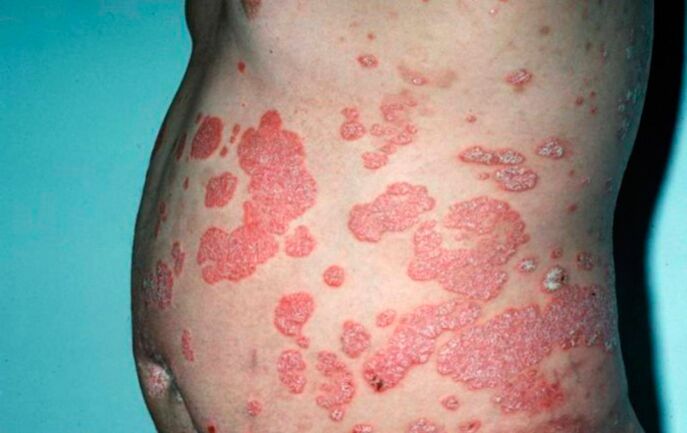
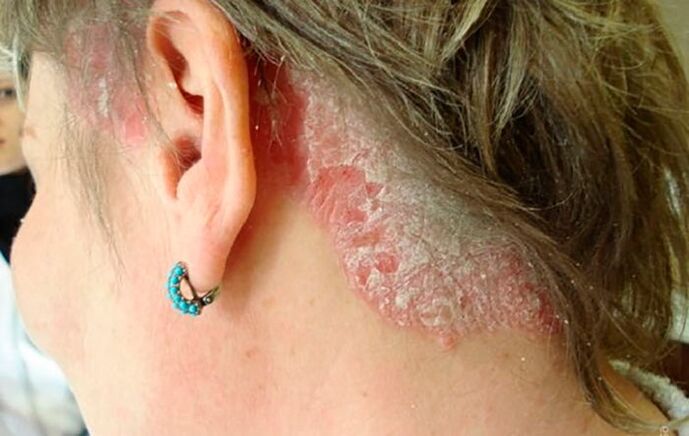
With this disease, on the skin appear papules and plaques. The patches are small, well-defined spots on the skin that are pink or reddish in color with small light-colored scales. The arrays have different shapes, but they are usually round or oval. They can be located anywhere on the human body, but are more commonly observed on the large joints, on the sacrum and lower back, under the hairs on the head.
Psoriatic papules are characterized by rapid growth with the formation of patches several centimeters in size, which then coalesce into large skin lesions.
How is psoriasis diagnosed?
The following indicators are important for diagnosis:
- If you try to scrape the papule, the scab easily peels off, forming a "stearin spot".
- A red glossy surface appears on the skin - the end membrane of the spot;
- If you continue to scrape off the stain, then blood stains will appear on the surface - "blood mist".
Stages of Psoriasis
For the rash accompanying the disease, the following stages of development are characteristic:
- Advanced stage (small papules appear, grow over time and merge into larger nodules);
- Static phase (arrays grow and do not change for a certain time);
- Regressive stage (the rash turns pale, thins and disappears from the surface of the skin).
Depending on the condition, the disease can last a long time.
For the early stages of the rash, the Kebner effect is characteristic: new psoriatic lesions appear on the affected skin site after about a week.
During periods of skin remission in the elbow or knee joint area, isolated so-called "mission" patches may remain.
Types of Psoriasis
There are several types of diseases:
- Secretory form: with it, the appearance of vesicles and luminosity of papules with yellow scales on their surface;
- Cystic form: small papules located in the cystic foramen;
- Palmar-plantar psoriasis: with it, the skin of the soles and palms is covered with cracks and scales, psoriatic plaques are visible on it;
- Seborrheic psoriasis: localized mainly on the scalp;
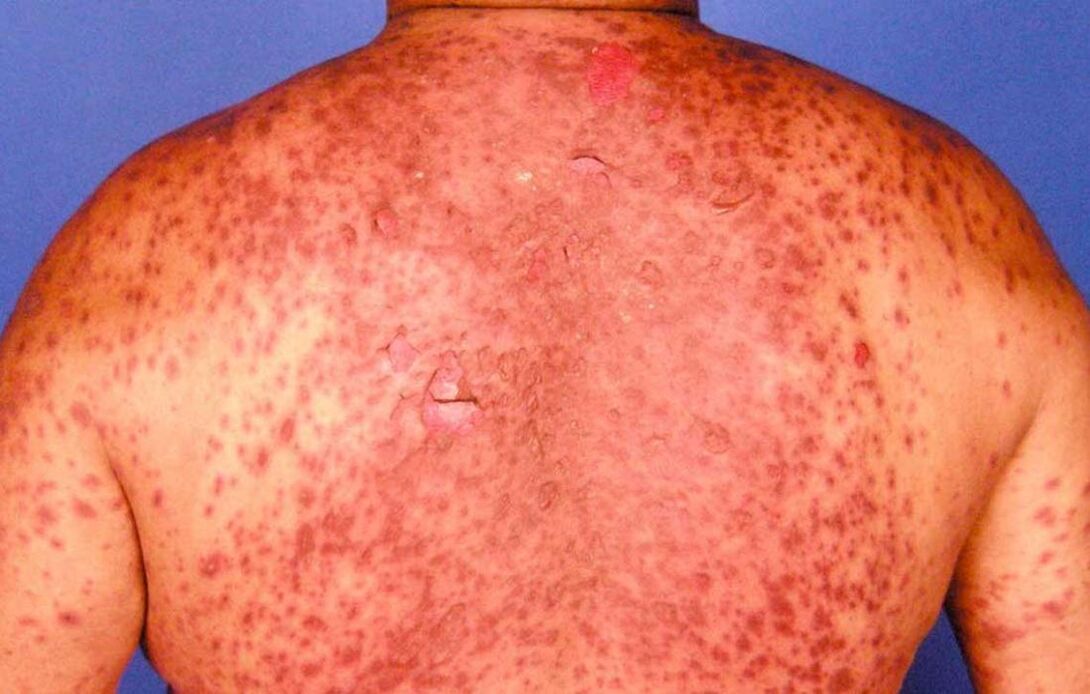
- Erythema psoriatic. In this form, the disease is very difficult to cure, the entire skin surface is scaly, peripheral lymph nodes are increased, fever, itching, sleep disturbances, blood and urine changes are observed;
- Arthritis psoriasis: affects and deforms the joints, limiting their movement. It is characterized by severe pain and swelling in the affected joint area. This is a very painful form of psoriasis that often leads to disability.
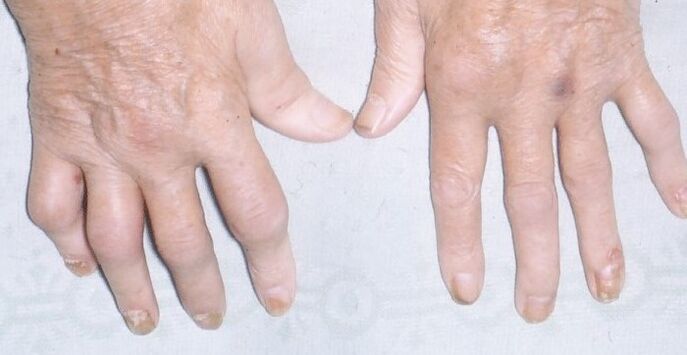
In all forms of psoriasis, the nails change: they become opaque, thicken, and appear as small spots as if they were poked by a needle.
The disease lasts for many years with periods of decline and improvement in health, seasonal in nature: exacerbation in the cold season and remission in the warm season.
Treatment of psoriasis
Psoriasis should be treated under the supervision of a physician in dermatology. Treatment is indicated by the optimal combination of therapeutic drugs with ointments and physiotherapy, as well as the restriction of animal fats and carbohydrates in food, alcohol and spicy foods.
Patients should be under the supervision of a doctor and they need an annual spa treatment. With psoriasis, you should visit radon springs and hydrogen sulfide baths, swim in the sea, and sunbathe.

























